Concepts
All three Apache Kafka Sink Connectors provided by LittleHorse Connect have similar structure and behaviors.
- Expected Apache Kafka message structure.
- Required configurations for the LittleHorse Clients.
- Installation.
Background: Kafka Sink Connectors
All three Connectors are Sink Connectors, which means they read an Apache Kafka Connect SinkRecord. See the Kafka code for SinkRecord and the super class ConnectRecord.
A ConnectRecord has a key and a value, both of which have a Kafka Connect Schema. A Schema specifies either a primitive type or a Struct, which is a collection of fields and typed values.
The diagram below shows the lifecycle of a record as it moves from a Kafka Topic, through a Kafka Sink Connector, and into the external system:
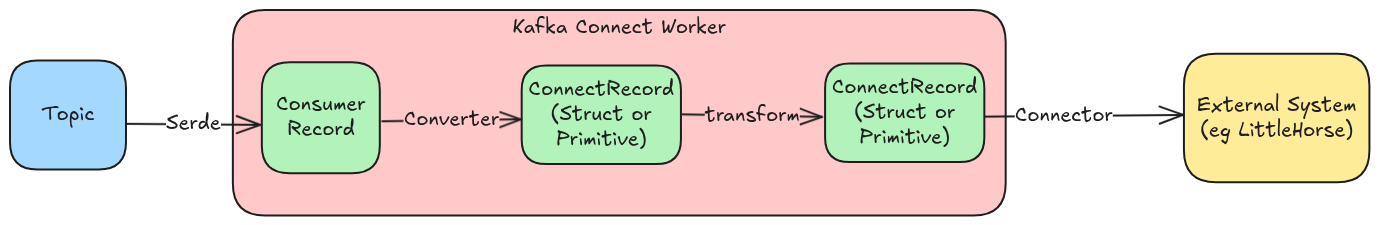
When the Kafka Connect worker polls records from the Kafka Topic, each record goes through the following steps:
- A consumer inside the Kafka Connect Worker gets a
ConsumerRecord. - The configured
Converter(part of the Connector configuration) converts theConsumerRecordinto aConnectRecord. - Zero or more Kafka Connect Transformations are applied to the
ConnectRecord, according to the Connector configuration. Transforms can rename, drop, or add fields, and even filter out messages. - Lastly, the final
ConnectRecordis passed into the Sink Connector, which processes it by sending it to an external system.
In the case of LittleHorse Connect, the system in step 4 is none other than the LittleHorse Kernel!
Processing Messages
The LittleHorse Connectors all make a GRPC request, utilizing both the message key and message value.
LittleHorse Variable Types
In the LittleHorse Kernel, all values are represented by the VariableValue protobuf message.
The following table explains how Kafka Connect ConnectRecord keys and values are mapped into LittleHorse VariableValues. As of LittleHorse 0.14, the following types are supported in LittleHorse:
| LittleHorse Type | Java Type | Kafka Connect Schema Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
INT | Long or Integer | INT64, INT32, INT16, or INT8 | LittleHorse SDK's always cast it to 64-bits. |
DOUBLE | Double or Float | FLOAT32 or FLOAT64 | LittleHorse SDK's always cast it to 64-bits. |
STR | String | STRING | |
BYTES | byte[] | BYTES | |
JSON_ARR | List | ARRAY | Arrays in LittleHorse are stored in JSON format. |
JSON_OBJ | Map | MAP or Struct | Objects in LittleHorse are stored in JSON format. |
BOOL | Boolean | BOOLEAN |
GRPC Payloads
The following table explains how each LittleHorse Sink Connector behaves, including which GRPC request it makes, how it utilizes the ConnectRecord key, and how it utilizes the ConnectRecord value.
| Connector | GRPC Request | Field Set by Key | Field Set by Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
WfRunSinkConnector | rpc RunWf | id | variables | The ConnectRecord's value must be a Kafka Connect MAP or STRUCT. Each entry becomes a variable in the RunWfRequest. |
ExternalEventSinkConnector | rpc PutExternalEvent | wf_run_id | content | |
CorrelatedEventSinkConnector | rpc PutCorrelatedEvent | key | content | The ConnectRecord key cannot be null |
If the ConnectRecord key is set, then all of the connectors are idempotent. Note that the CorrelatedEventSinkConnector requires that the key is set.
Developer Notes
The following section contains useful notes for developers using the connectors.
Data Types
Note that LittleHorse kernel is data type aware. When reading data from the Kafka topic with any of our three Connectors, the data types in the topic correlate with the data LittleHorse kernel expects.
A common issue is with the Boolean data type. If LittleHorse kernel expects a Boolean type "True" or "False", this must match Boolean data type in the schema of the topic.
For testing it is common to use kafka-console-producer.sh tool provided by Apache Kafka, this tool can only produce String or Integer values. In order to accuratly send a primitive type other than String or Integer you must use a converter in the Kafka Connect connector configuration.
Example:
{
"name": "external-identity-verified",
"config": {
"tasks.max": 2,
"topics": "names",
"connector.class": "io.littlehorse.connect.ExternalEventSinkConnector",
"key.converter": "org.apache.kafka.connect.storage.StringConverter",
"value.converter": "org.apache.kafka.connect.storage.StringConverter",
"lhc.api.port": 2023,
"lhc.api.host": "localhost",
"lhc.tenant.id": "default",
"transforms": "Cast",
"transforms.Cast.type": "org.apache.kafka.connect.transforms.Cast$Value",
"transforms.Cast.spec": "boolean",
"external.event.name": "identity-verified"
}
}
Note the lines that begin with "transforms", with those we are casting the String data type sent by kafka-console-producer.sh to the primitive Boolean.
For more information:
- https://docs.confluent.io/kafka-connectors/transforms/current/cast.html
- https://docs.confluent.io/kafka-connectors/transforms/current/overview.html
Converters
These connectors support Protobuf, Json and Avro through converters.
More about converters at Kafka Connect Converters
External Secrets
Kafka connect ensures provisioning secrets through the ConfigProvider interface, so these connectors support external secrets by default.
More about secrets at Externalize Secrets.