Executing WfSpecs
Now that you've created your first WfSpec, let's explore the different ways to run it. LittleHorse provides multiple methods to execute WfSpecs, each suited for different use cases.
This tutorial assumes you have completed the Your First WfSpec guide.
Executing with lhctl
The simplest way to execute a WfSpec is using the command-line interface. The lhctl command provides a quick way to execute and monitor WfRuns:
# Execute the `WfSpec` with a name parameter
lhctl run quickstart name Obi-Wan
You'll see output like:
{
"id": {
"id": "69881bf9aaf84c2f84bdde7ceb2dd105"
},
"wfSpecId": {
"name": "quickstart",
"majorVersion": 0,
"revision": 0
},
"oldWfSpecVersions": [],
"status": "RUNNING",
"greatestThreadrunNumber": 0,
"startTime": "2025-01-07T01:53:47.212Z",
"threadRuns": [
{
"wfSpecId": {
"name": "quickstart",
"majorVersion": 0,
"revision": 0
},
"number": 0,
"status": "RUNNING",
"threadSpecName": "entrypoint",
"startTime": "2025-01-07T01:53:47.296Z",
"childThreadIds": [],
"haltReasons": [],
"currentNodePosition": 1,
"handledFailedChildren": [],
"type": "ENTRYPOINT"
}
],
"pendingInterrupts": [],
"pendingFailures": []
}
The lhctl command is perfect for development and testing scenarios. It's also commonly used in CI/CD pipelines for automation.
Executing from the Dashboard
LittleHorse provides a visual interface for running and monitoring WfSpec and WfRuns:
- Navigate to
http://localhost:8080in your browser - Click on the "quickstart"
WfSpec - Click "Execute"
- Enter "Obi-Wan" in the name field
- Click "Execute Workflow"
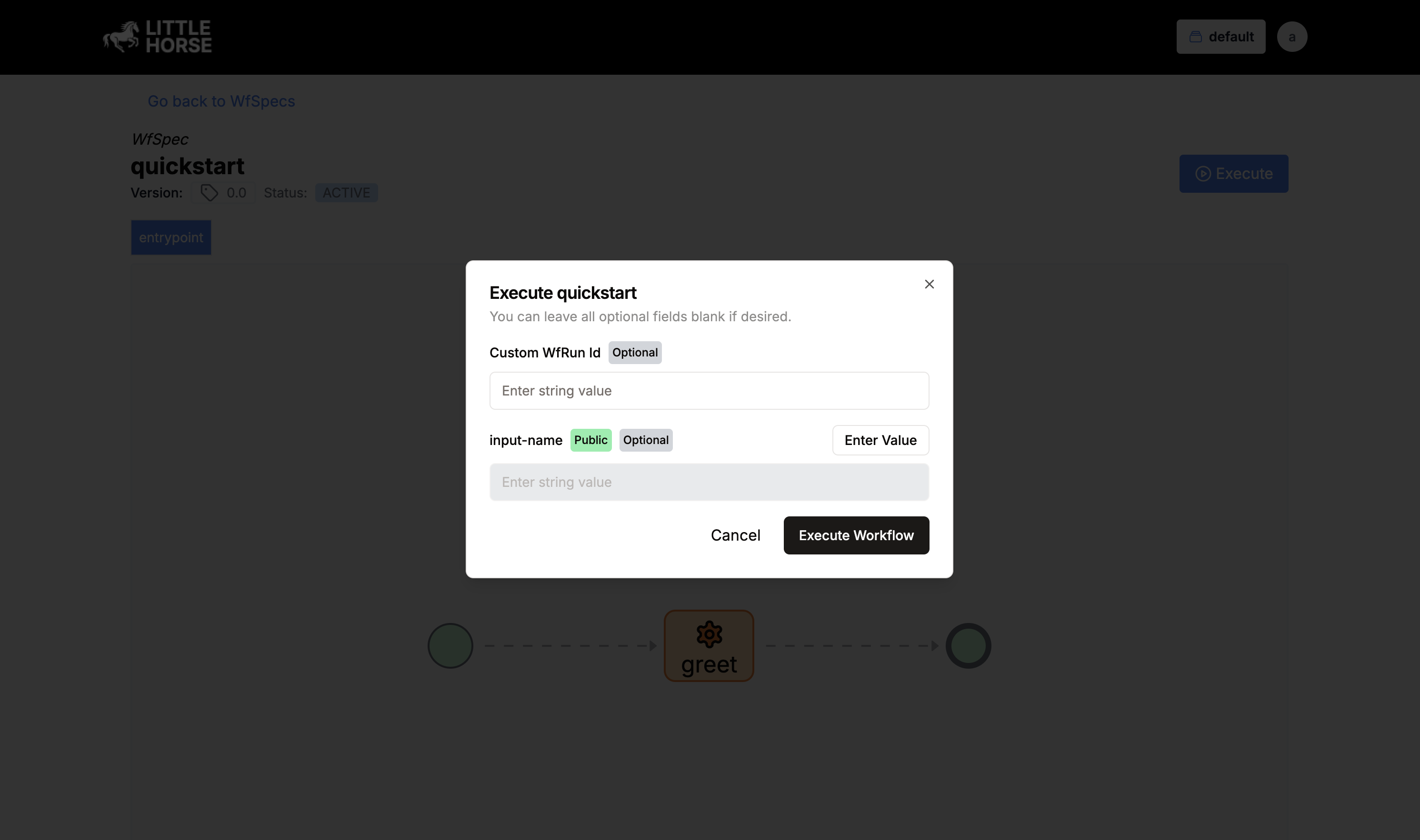
The 'Execute WfRun' modal in LH Dashboard
The dashboard will show you the WfRun's execution status in real-time, making it ideal for debugging.
Executing with the Java SDK
For production applications, you'll typically want to execute WfSpecs programmatically. Create a new file called RunWorkflow.java:
package io.littlehorse.quickstart;
import io.littlehorse.sdk.common.config.LHConfig;
import io.littlehorse.sdk.client.LHClient;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Initialize the client
LHConfig config = new LHConfig();
LHClient client = new LHClient(config);
// Run the workflow
String wfRunId = client.runWorkflow(
"quickstart",
java.util.Map.of("name", "anakin"),
null
).getId();
System.out.println("Started workflow with ID: " + wfRunId);
}
}
The Java SDK provides the most flexibility for executing WfSpecs. You can integrate it into your existing applications and handle WfSpec execution programmatically.
Choosing the Right Method
Each method has its ideal use case:
| Method | Best For |
|---|---|
lhctl | Development, testing, and CI/CD pipelines |
| Dashboard | Debugging, monitoring, and team collaboration |
| Java SDK | Production applications and system integration |
Remember, all methods interact with the same LittleHorse server, so you can mix and match them based on your needs.
Wrapping Up
You've learned how to execute WfSpecs using different methods and monitor their execution. In the next lesson, we'll dive deeper into debugging WfRuns and handling errors.
If you haven't already:
- Join the LittleHorse Slack Community
- Give us a star on GitHub
- Check out our documentation